Mushrooms have become a staple in health and wellness, not only for their unique flavor profiles but also for their powerful medicinal properties. They are packed with nutrients, antioxidants, and bioactive compounds that can support the immune system, brain health, and overall vitality. However, not all mushrooms are created equal. The method by which they are cultivated significantly impacts their quality, safety, and potency. This article explores why lab-grown mushrooms are a superior choice compared to wild or log-grown varieties, focusing on key aspects such as quality control, contamination prevention, and consistency in bioactive compounds.
1. Quality Control: Precision and Purity
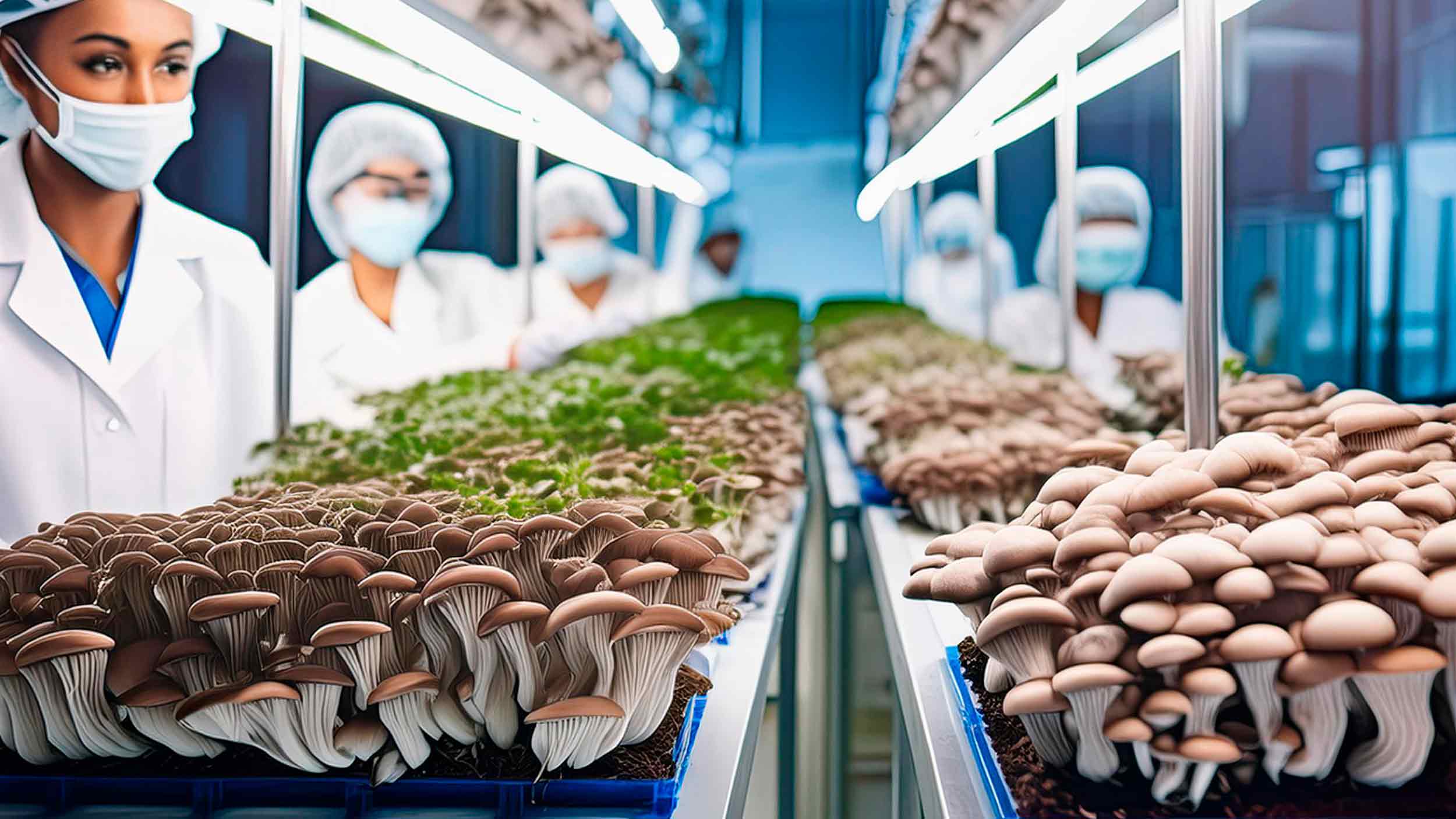
One of the most significant advantages of lab-grown mushrooms is the level of quality control that can be maintained throughout the cultivation process. Unlike wild or log-grown mushrooms that are subject to the unpredictable forces of nature, lab-grown mushrooms are produced in controlled environments. This controlled setting ensures that the mushrooms receive the optimal conditions for growth, such as the right temperature, humidity, and light. By eliminating external variables, lab-grown mushrooms are not only more consistent in appearance and texture but also in nutritional value and potency.
Wild mushrooms, on the other hand, are exposed to environmental pollutants, soil contaminants, and other unpredictable elements that can compromise their quality. Log-grown mushrooms, while slightly more controlled than wild mushrooms, are still susceptible to varying weather conditions and contamination from the surrounding environment. In contrast, lab-grown mushrooms undergo rigorous quality checks at every stage of their growth cycle, ensuring that they meet the highest standards of purity and safety.
2. Contamination Prevention: No More Pests and Insect Droppings
One of the lesser-known but highly concerning issues with wild and log-grown mushrooms is the risk of contamination from pests and insects. In the wild, mushrooms are exposed to a variety of pests such as insects, snails, and rodents. These creatures can leave behind droppings, urine, or even directly feed on the mushrooms, leading to contamination with harmful bacteria, parasites, and pathogens. This not only affects the aesthetic quality of the mushrooms but also poses potential health risks to consumers.
Log-grown mushrooms, while more protected than wild ones, are still grown in outdoor or semi-outdoor environments where insects and pests can access them. The logs themselves can harbor mold, bacteria, or fungi that are detrimental to the mushrooms’ quality.
Lab-grown mushrooms, however, are cultivated in clean, sterile environments where the risk of contamination from pests, insects, and their droppings is virtually eliminated. These controlled environments use advanced filtration systems and sterile techniques to maintain an environment free of pests and pathogens, ensuring that the final product is clean, safe, and of the highest quality.
3. Consistency in Bioactive Compounds: Reliable Health Benefits
The medicinal properties of mushrooms, such as immune support, anti-inflammatory effects, and cognitive enhancement, are largely due to their bioactive compounds like beta-glucans, polysaccharides, and triterpenoids. The concentration and potency of these compounds can vary significantly in wild or log-grown mushrooms due to environmental factors such as soil quality, weather, and exposure to sunlight.
Lab-grown mushrooms are cultivated under controlled conditions that can be optimized to produce higher concentrations of these bioactive compounds. By precisely controlling factors such as substrate composition, humidity, temperature, and light exposure, growers can enhance the production of specific compounds that are beneficial for health. This leads to a more reliable product where the consumer can trust that each batch of mushrooms delivers the promised health benefits.
In wild or log-grown mushrooms, there is often no way to guarantee consistency in the levels of these beneficial compounds. This variability can affect the efficacy of the mushrooms when used for medicinal purposes, making lab-grown varieties a more dependable choice for those seeking specific health outcomes.
4. Sustainability and Environmental Impact: A Greener Choice
Lab-grown mushrooms are not only superior in terms of quality and safety, but they also present a more sustainable option for mushroom cultivation. Wild mushroom foraging, while seemingly eco-friendly, can disrupt local ecosystems, harm native plant species, and deplete natural resources. Overharvesting wild mushrooms can also endanger certain species and impact biodiversity.
Log-grown mushrooms, although less invasive, still require the cutting down of trees to provide the necessary logs for mushroom growth. This can contribute to deforestation and habitat loss if not managed responsibly.
Lab-grown mushrooms, on the other hand, can be produced using sustainable and renewable substrates such as agricultural waste, sawdust, or other organic materials. The controlled environments also allow for efficient water use, reduced land use, and minimized waste, making lab-grown mushrooms a more environmentally friendly choice. Moreover, the reduced need for pesticides and other chemical inputs further lowers the environmental footprint of lab-grown mushroom production.
5. Speed and Efficiency of Production: Meeting Market Demand
Another advantage of lab-grown mushrooms is the speed and efficiency with which they can be produced. Wild mushrooms are subject to seasonal availability and varying weather conditions, while log-grown mushrooms require time for the logs to colonize and fruit, often taking several months to produce a harvest.
In contrast, lab-grown mushrooms can be cultivated year-round in climate-controlled environments, ensuring a steady and reliable supply to meet market demand. This not only benefits consumers by providing consistent access to high-quality mushrooms but also supports the industry by reducing the risks associated with crop failure due to adverse weather or environmental conditions.
6. Customization and Innovation: Tailored to Specific Needs
The controlled environment of lab cultivation also allows for customization in mushroom growth. Growers can manipulate growing conditions to produce mushrooms with enhanced flavors, textures, or nutritional profiles tailored to specific consumer needs. For example, certain substrates can be enriched with minerals or nutrients to enhance the mushrooms’ health benefits.
This level of customization is not possible with wild or log-grown mushrooms, where the natural environment dictates the characteristics of the mushrooms. The ability to innovate and produce tailored products makes lab-grown mushrooms a versatile option for both culinary and medicinal applications.
7. Reduced Risk of Allergens and Toxins
Wild mushrooms carry an inherent risk of containing toxins, heavy metals, or allergens absorbed from their natural environment. They can also easily be confused with poisonous varieties when foraged, posing a significant risk to consumers. Even log-grown mushrooms can sometimes absorb unwanted substances from the logs or the surrounding environment.
Lab-grown mushrooms are cultivated under strict conditions that minimize the risk of exposure to allergens, toxins, and heavy metals. This controlled process ensures that the mushrooms are safe for consumption, especially for those with sensitivities or allergies.
Conclusion
Lab-grown mushrooms clearly stand out as the superior choice when considering quality control, safety, consistency, sustainability, and innovation. By eliminating the variables associated with wild or log-grown mushrooms—such as pests, contaminants, and inconsistent bioactive compounds—lab-grown mushrooms offer a cleaner, more reliable, and environmentally friendly alternative. For consumers looking to maximize the health benefits of mushrooms while minimizing potential risks, lab-grown varieties provide a modern solution that aligns with the growing demand for high-quality, sustainable, and safe food products.



Why Medicinal Mushroom Full-Spectrum Powder is Better Than Extracts: The Truth About Freeze-Dried Water and Alcohol-Based Products
Lion’s Mane Mushroom: A Natural Boost for Brain Health